Learning About the Symptoms, Causes, and Living With Crohn’s and Colitis
A person’s way of life tends to be affected negatively by chronic health disorders. Digestive problems rank among the most serious gastrointestinal ailments. These include Crohn’s colitis disease along with ulcerative colitis, which is a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). These diseases are both physically and emotionally draining, to say the least.
We will go into detail on what the symptoms of crohn’s colitis are, what the difference between crohn’s and colitis is, the role of the immune system, complications like skin manifestations of crohn’s disease, and how inflammatory bowel syndrome symptoms (which are commonly mistaken for IBD) differ. Furthermore, we will discuss signs and symptoms of crohn’s disease, available treatment options, and how people can cope with these conditions.
What is Crohn’s Colitis Disease?
Both crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are categorized under inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) but exhibit unique characteristics.
• Crohn’s disease can impact any section of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, that is, the mouth and anus, but most frequently affects the last part of the small intestine and the start of the colon. Inflammation in the intestines is patchy and often deep.
• Ulcerative colitis is restricted to the colon (large intestine) and rectum. Most of the time inflammation of the colon is superficial, as it only impacts the innermost layer.
When we talk about Crohn’s colitis disease, it means the person suffers from Crohn’s disease specifically affecting colon which may make it difficult to differentiate it from ulcerative colitis. But the behavior, distribution, and complications of the disease tend to differ.
Crohn’s Disease Signs And Symptoms
Symptoms of Crohn’s tend to differ from one individual to another and also depend on which area of the rest of the intestine is affected. Some hallmark signs include.
These symptoms could and do include
• Chronic diarrhea
• Stomach aches (abdominal pains) and contractions (cramping)
• Unintentional weight changes (loss)
• Tiredness and weakness (low energy)
• Increase in temperature (fever)
• Decreased interest in food (Loss of appetite)
• Presence of vomit in stool (Blood in the stool)
These symptoms usually come with flare-ups, chronic periods when the condition exacerbates and intermittently goes through phases of relatively borderline/post-exacerbation periods where the condition and symptoms vanish for some time.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease: When It Targets the Colon
When Crohn’s disease affects the large intestine (the colon), patients may show signs similar to those of ulcerative colitis. Symptoms of Crohn’s colitis include:
• Chronic severe diarrhea with blood
• Urgent and frequently needed trips to the bathroom
• Bleeding from the anus
• Painful sensations radiating from the lower abdomen
• Declining weight
• Stool with mucus
Unlike ulcerative colitis, inflammation seen with Crohn’s disease is sometimes patchy (i.e., inflammation is not continuous within a region) and goes further into the level of the bowel wall, with a higher possibility of other severe problems such as strictures (narrowing of the intestines), fistulas (abnormal connections between organs), and even abscesses.
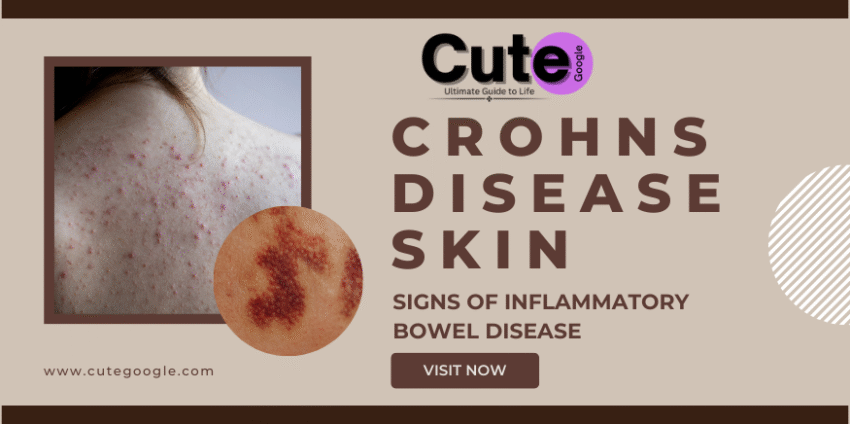
Skin Complications of Crohn’s Disease: When IBD Extends Beyond the Intestine
Skin complications of Crohn’s disease are something that many individuals tend to overlook but are very much part of the disease and often painful. Because Crohn’s is a systemic autoimmune disease, it doesn’t only involve the intestines; it leads to inflammatory changes in other systems like the skin.
Some of the common skin issues related to Crohn’s include:
• Erythema nodosum: Tender red bumps, usually on the shins
• Pyoderma gangrenosum: Painful skin ulcers, which may begin as minor sores
• Skin tags or fissures around the anal area
• Mouth ulcers
Regardless of whether there is gut symptomatology coupled with skin symptoms flaring, these symptoms may arise in flares or persist irrespective of gut control. The appropriate level of dermatological intervention is needed with regard to skin manifestations for proper care.
Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome Symptoms: IBD and IBS
The difference between IBD and IBS is significant and should be highlighted. The main area of confusion tends to be inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); these are distinct.
• IBD (which encompasses Crohn’s and colitis) includes chronic inflammation with associated pathology of the bowel.
• IBS, or irritable bowel syndrome, is functional in nature and belongs to GIT disorders. It is non-inflammatory and non-destructive, though still unpleasant.
Symptoms commonly associated with inflammatory bowel syndrome may bear some resemblance to IBD symptoms, including
• Abdominal cramps
• Bloating
• Diarrhea or constipation
• Gas and mucus in stool
The absence of characteristic symptoms such as bleeding, fever, or weight loss eliminates the diagnosis of Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis and distinguishes this from IBS.
Causes and Risks of Crohn’s and Colitis
The specific causes of Crohn’s colitis disease are still under study, but it is likely a combination of the following:
• Genetics: One or more family members having IBD increases the chances of getting it.
• Immune System: An autoimmune disease in which one’s immune system misidentifies and attacks healthy tissue in the gastrointestinal tract.
• Environmental factors: Diet, smoking, stress, and at times even some medications can worsen the symptoms.
• Gut Health Deterioration: Problems with the body’s bacteria may contribute to the disease.
Diagnosis of Crohn’s Colitis Disease
Diagnosing Crohn’s colitis disease can be complicated, as it is with
• A blood test where anemia or blood inflammation is checked
• Taking a stool sample to ensure there is no infection
• Colonoscopy for looking at the colon with a camera and taking tissue samples (biopsies)
• Using Cat Scans and MRI’s to identify lesions and inflammatory processes in the soft tissues
These procedures allow us to rule out anything else that could cause inflammation not related to Crohn’s. Because symptoms are similar, accurate differentiation is crucial to make the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Crohn’s and Colitis
Currently, there is no known way to completely cure either form of colitis, but there are several treatment options that can help in decreasing the inflammation, alleviating the irritable bowel disturbing symptoms, and maintaining long-term periods of controlled disease activity.
1. Medications
• Aminosalicylates: Usually prescribed for mild-to-moderate inflammation.
• Corticosteroids: Used to combat short-term flare-ups.
• Immunosuppressants: Assist in calming the immune system.
• Biologic therapies: Treat particular proteins responsible for inflammation (e.g., anti-TNF drugs).
• Antibiotics: Treats infections or fistulas.
2. Diet and Nutrition
While diet doesn’t cause Crohn’s or colitis, it is crucial for symptom management. Some people benefit from
• Low fiber intake during flare-ups.
• Elimination of dairy or gluten.
• Monitoring trigger foods through a food diary.
• Nutritional supplements to help with deficiencies.
3. Surgery
Surgery may be needed if there are strictures or abscesses and medication isn’t working. This surgery seeks to remove the problematic, damaged, and non-functional portions of the intestine.
Living with Crohn’s And Colitis.
Being diagnosed with Crohn’s colitis disease is a lot to take in, but so long as there is a treatment plan in place, it will ensure that many people go on to live full and active lives.
Tips for managing daily life include:
– Keeping a strict medication schedule
– Attending regular doctor visits
– Engaging in yoga, meditation, or other stress alleviating activities
– Enrolling in a support group
– Anticipating meal and bathroom access when going out
Because flare-ups are unpredictable, developing a lifestyle that includes scheduled rest periods, healthy food choices, and focus on emotional well-being is vital.
Closing Remarks
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease and Crohn’s colitis can significantly impact one’s emotional and physical health. Persistent diarrhea, painful skin problems, and debilitating fatigue are some of the symptoms people share, but it’s important to recognize that effective treatment does exist.
Illustrating the difference between IBD and inflammatory bowel syndrome symptoms, understanding complications such as Crohn’s disease skin problems, and collaborating with a healthcare professional for a suitable treatment strategy are essential in effectively managing this chronic condition.
While the journey may be lengthy, it certainly isn’t devoid of hope. Ongoing research, combined with strong supportive care and a foundational understanding of one’s body, makes it possible to regain control over one’s life and be empowered in decisions regarding one’s health and well-being.